High
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
1
The specific heat capacity of a material is defined as the
energy needed to raise the
temperature of 1 kg
of the material by 1oC.
|
material
|
iron
|
aluminium
|
copper
|
lead
|
concrete
|
|
specific heat capacity (J/kg/oC)
|
390
|
900
|
490
|
130
|
850
|
The table shows a range of materials and their specific heat
capacities.
Hassan wants to design a container in which he can heat
water. He has containers made out of
the materials shown in the table.
(a)(i) Draw a bar
graph to display the specific heat capacities for these materials.
[2]
(ii) If each container has a mass of 1 kg, which
material would need the least energy to heat it
through 1oC? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iii) Hassan
decides not to choose a container made out of this material.
Why not?
(1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(Continued…)
QUESTIONSHEET
1 CONTINUED
(b) (i) A copper
container of mass 500g is used to heat water.
Using the equation:
Energy
supplied = mass ´
specific heat capacity ´
rise in temperature
(J)
(kg) (J/kg/oC) (oC)
calculate
the amount of energy needed to raise its temperature from 20oC to 100oC.
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(ii) Calculate the amount of energy saved by using
the copper container rather than an aluminium container of mass 500g.
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
TOTAL / 9
High
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
2
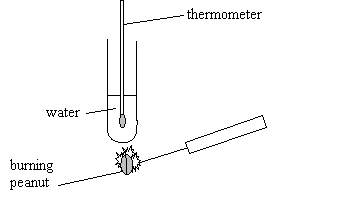
Debbie and Asha are using a burning peanut to heat water in a
boiling tube.
(a) What can they find out about the peanut by doing this
experiment?
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(b) (i) The equation:
Energy
supplied = mass x specific heat capacity x
temperature rise
(J) (kg) (J/kg/oC) (oC)
can be used to calculate the energy supplied to the water in
the boiling tube.
The temperature of the water rose from 20oC to 70oC. If there were 20g of water in the tube, and
the specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J/kg/oC, calculate the
energy supplied to the water.
(2 marks, 3 lines)
(ii) The amount of energy stored
in a peanut is much greater than this.
Give two reasons why all the
energy from the peanut did not go into
heating the water.
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(c) At the end of the experiment, the outside of the tube was
covered in a black deposit.
(i) What
was this? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) Where had it come from? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
TOTAL / 7
High
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
3
The diagram shows a house without any insulation. The percentage of the energy lost from
different parts of the house during the year is shown.

(a) The total cost of the energy lost during the
year is £1000. This represents 35% of
the total heating bill for the
house.
(i) Calculate the cost of heating the house for
one year.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(ii) Calculate the cost of the energy wasted
through the floor.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(iii) Suggest
one way of reducing the amount of heat energy escaping through the door other
than draught proofing.
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(b)The table shows some types of methods used to conserve
energy, their installation costs and the
amount of money that this method would save in
a year. Assume each method reduces heat loss by 80%
|
Place of installation
|
Method of insulation
|
Purchase cost (£)
|
Cost of energy wasted per year (£)
|
Cost of energy saved per year
(£)
|
|
Roof
|
Rock-wool or
Fibre-glass in loft
|
250
|
200
|
|
|
Walls
|
Cavity wall filling
|
1000
|
350
|
|
|
Windows
|
Double glazing
|
3500
|
150
|
120
|
|
Doors
|
Draught-proofing
|
5
|
150
|
|
(i) Complete the table by calculating the cost
of the energy saved in one year for each method of insulation (The
double-glazing has been done for you).
[3]
(Continued...)
QUESTIONSHEET
3 CONTINUED
(ii) Calculate
the length of time needed to payback the initial purchase cost of
Double-glazing. (Assume the cost of the energy does not change).
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iii) Which type of insulation would you install
first? Explain why.
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
TOTAL / 12
High
Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 4
(a) Architects calculate
heat loss from houses using a factor called the U-value.
They use the
following formula:
Heat loss
per second = area x temperature difference x
U-value
(W) (m2) (oC)
What are the units
of the U-value?
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(b)Below are some
U-values for different parts of the house.
|
Part of house
|
U-value
|
|
Single-glazed window
|
5.5
|
|
Double-glazed window
|
3.0
|
|
Roof
|
2.0
|
|
Insulated roof
|
0.5
|
|
Cavity wall
|
1.5
|
|
Insulated cavity wall
|
0.5
|
An insulated roof
measures 10 m by 8 m. The temperature
inside is 20oC and outside is 2oC.
Calculate the heat
loss per second through the roof.
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
TOTAL / 4
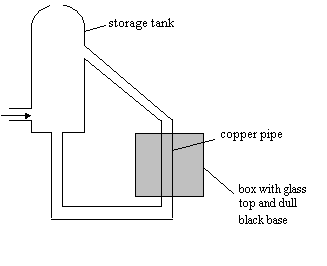
High Demand
Questions QUESTIONSHEET
5
Some people have solar panels to heat their water mounted on
their roofs.
The diagram below shows the set up of a solar panel


(a) Explain why the
surface is a dull black.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(b) Why is it covered
with glass?
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(c) (i) Why are the pipes arranged in a zig-zag
pattern?
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(ii) Why
should the pipe linking the solar panel to the hot water tank be as short as
possible?
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(d) (i) What makes the water move through the pipes?
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) Why
is the storage tank usually fitted higher than the panel?
............................................................................................................................................................ [1] .................................................................................................................................................................. (1)
(e) The house would
normally have an alternative method of heating the water. Explain why. (1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
TOTAL / 9
High Demand
Questions QUESTIONSHEET
6
(a) Explain why birds
fluff up their feathers in cold weather.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(b) Tramps will often
wrap themselves in newspaper at night.
Why does this help
them to keep warm?
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(c) Design an experiment or series of experiments
to compare the insulating properties of feathers and of newspaper. Mention the controls you would use to ensure
that the experiments were fair.
(8)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [8]
TOTAL / 11
High
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
7
The energy needed to change the temperature of a substance
depends on the mass of the substance, the temperature and the specific heat
capacity of the substance.
(a) Calculate the amount
of energy needed to change the temperature of:
(i) 500 g of water by 5oC (specific heat capacity of water is 4200
J/kg oC)
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(ii) 100 g of aluminium from 100C to
300C (specific heat capacity
of aluminium is 880 J/kg oC)
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(b)A 4 kg lump of
iron is given 20 kJ of energy. It rises
in temperature by 10oC.
Calculate the
specific heat capacity of iron.
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(c) At the seaside on a
hot day, the sand feels warm, but the sea is cold. Explain this.
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 11
High
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
8
(a) A kettle has a power
rating of 3 kW. 1.5 kg of water at 5oC are put in the kettle.
Assuming no heat is
lost:
(i) how
much energy is needed to boil the kettle?
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(ii) how long will the kettle take to boil?
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(the specific heat
capacity for water is 4200 J/kg 0C)
(b) How long would the
kettle take to boil if 2 kg of ice at 0oC was put in it?
(latent heat of
fusion of ice is 334 000 J/kg)
(4)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [4]
TOTAL / 10
Medium
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
9
(a) All metals expand
when they are heated, but by differing amounts.
Aluminium expands
more than copper, which expands more than iron.
Draw labelled
diagrams to show what you would expect to see when the following bimetal strips
are heated
to 300 oC:
(i) Copper and iron
(2)
[2]
(ii) copper and aluminium
(2)
[2]
(b)(i) Explain how bimetallic strips can be used to
make a thermostat.
(4)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [4]
TOTAL / 8
Medium
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
10
(a) Explain how the
following methods of insulating a house help to reduce heat loss.
(i) double glazing.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(ii) lining the loft with fibre glass.
(2)
..................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(iii) the use of thick carpets.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(b) Air is a very poor
conductor of heat. Why is air replaced by foam in cavity wall insulation?
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(c) Explain why a string
vest keeps a person warm, even though it is only a collection of holes.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 10
Medium
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
11
(a) The linear expansivity of a substance is the
amount by which one metre length will increase for every one degree Celsius
rise in temperature. Engineers can use this to work out how much their
materials will expand over the range of temperature in which they are to be
used.
(i) Why
is it important to know this when building a bridge?
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(ii) The linear expansivity of steel is 0.000 012
m per oC.
What will be
the length of a 500 m steel bridge if the temperature rises by 50 oC?
(3)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(b) The linear
expansivity of copper is 0.000 02 m per oC and that of aluminium
0.000 03 m per oC.
Which of the will
expand most, 50 m of copper heated by 40 oC or 50 m of aluminium
heated by 30 oC?
Justify your
answers by calculations.
(4)
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [4]
(c) How was the idea of
expansivity used in fitting metal tyres to wooden cart wheels?
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 11
Medium
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
12
(a)Carol is testing 2 cups to see which has the best
insulating properties. The table shows
the data
when the same volume
of hot water is placed in each cup, and the temperature monitored for 10
minutes.
|
time (min)
|
0
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
10
|
|
paper cup
|
80
|
66
|
57
|
53
|
49
|
47
|
45
|
43
|
42
|
41
|
40
|
|
polystyrene cup
|
80
|
74
|
68
|
65
|
63
|
61
|
60
|
59
|
58
|
57
|
56
|




(i) Plot graphs of temperature and time for each
cup on the same axes. [5]

(Continued...)
QUESTIONSHEET
12 CONTINUED
(ii) How long did each cup take to cool from 80oC
to 70oC?
paper cup:
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
polystyrene cup: (2 marks, 2 lines)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iii) Which cup was
the best insulator? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iv) Explain your answer in (a)(iii). (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(b) Carol put lids on
the containers and repeated the experiment.
(i) What effect would you expect to see on her
results? (1
mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) Explain your answer in (b)(ii) (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
TOTAL / 11
Medium Demand
Questions QUESTIONSHEET
13
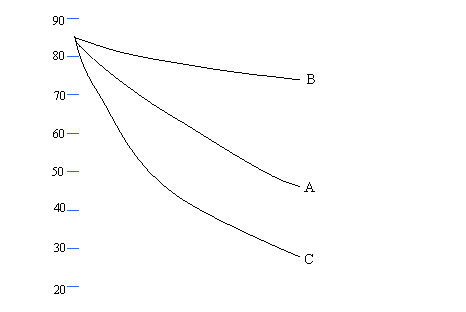
Mark sets up an experiment to investigate the heat loss from
containers covered with different materials.
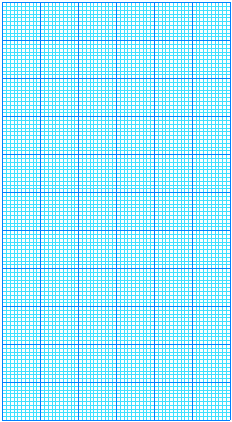
The graph
shows cooling curves for 3 containers.
A is a pyrex
beaker
B is a pyrex
beaker covered with aluminium foil
C is a pyrex
beaker painted black.
Each beaker
has a lid.
(a) (i) After what time is the temperature 80oC
for each beaker?
A: .............................................................................................................................................. [1]
B:
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
C:
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(ii) What is the temperature of each beaker after
10 minutes?
A:
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
B:
............................................................................................................................................. [1]
C: .............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(Continued...)
QUESTIONSHEET 13 CONTINUED
(b)(i) Which beaker is the best emitter of heat? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) How
is the heat being lost? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iii) Name two other ways that heat can be lost when
a body is hotter than its surroundings. (2
marks, 2 lines)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 10
Medium Demand
Questions QUESTIONSHEET
14
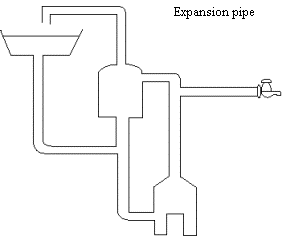
The diagram shows the important parts of a hot water system
in a home.

(a) (i) Name the main process whereby heat is transferred through the sides of the
hot water tank to
the surroundings.
(1)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(ii) Name
the main heat transfer process
whereby heat is transferred from the flames to the bottom of the boiler.
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(b) State why an
expansion pipe is needed.
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
For the following question use the theory of the arrangement
of particles in solids, liquids and gasses to help you to answer the question.
(c) Explain the
difference between the conduction and convection in solids liquids and gases.
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [4]
TOTAL / 8
Medium
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
15
Explain each of the following:
(a) a chimney and fire
help to ventilate a room.
(2)
..................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(b) a glider is able to
stay in the air.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(c) it is best to crawl
along the floor in a smoke-filled room.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(d) people wear light
coloured clothing in Summer.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(e) frost is more likely
to form on a clear night than on one which is cloudy.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 10
Medium
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
16
(a) Explain how
perspiration helps to keep you cool.
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(b) When walking on a
mountain in wet weather a person’s clothing became soaked.
Explain why this
could be dangerous to the person’s health.
................................................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [3]
(c) For each of the list
of conditions needed to dry clothes on a washing line as quickly as possible,
explain the science
behind them.
(i) the air should be dry
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(ii) the day should be windy
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(iii) large items such as sheets should be well
spread out.
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 12
Low
Demand Questions
QUESTIONSHEET 17
Mary has just received her gas bill for the winter
quarter. She is amazed at how high it
is.
Her friend Rita suggests that she should insulate her house.
(a) Why would insulation reduce her gas bill? (1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
|
where heat lost
|
walls
|
roof
|
windows
|
floors
|
|
% loss
|
40
|
35
|
15
|
10
|
(b) The table shows the percentage heat loss through parts of
a house.
(i) Draw a bar graph to display the results.
(2
marks, 0 lines)
[2]
(ii) Where is most energy lost from the house?
(1 mark, 1 line)
............................................................................................................................................................ [1]
(iii) Name the types of insulation she should
consider for each area:
walls:.......................................................................................................................................... [1]
roof:........................................................................................................................................... [1]
windows:.................................................................................................................................... [1]
floor:
.......................................................................................................................................... [1] ......................................................................................................................................................... (4
marks, 4 lines)
TOTAL / 8
Low
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
18
The diagram shows a vacuum flask. It is designed to keep heat from entering or leaving the flask.
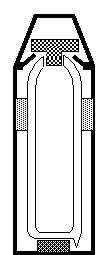
The table below shows a design feature to help to stop heat
being transferred and a type of heat transfer.
|
|
Design feature
|
|
Heat transfer process
|
|
|
|
Silvered inner walls
|
|
Conduction
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plastic stopper
|
|
Convection
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vacuum within inner cavity
|
|
Radiation
|
|
(a) Link the design
feature to the type of heat transfer that it is designed to reduce.
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(Continued...)
QUESTIONSHEET 18 CONTINUED
Below is a paragraph of text describing heat transfer. Insert a keyword into the blank spaces. The keywords are:-
CONDUCTION CONVECTION RADIATION.
The keywords may be used once, more than once or not at all.
(b) The main type of heat energy transfer in solids
is ________________.
The main type of energy transfer process in
liquids is __________________ .
The main type of heat energy transfer
process in gases is ____________________.
The Sun’s heat rays pass through outer
space towards Earth by a process called _______________.
[4]
(c) The diagram shows a
flask that has a crack in one of the inner walls.

Explain why the
flask did not work as efficiently.
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 8
Low
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
19
0 oC 20 oC 37 oC 50
oC 100 oC 176 oC 1530 oC
(a) From the list of temperatures given above, select the
most likely value for each of the following:
(i) the
boiling point of pure water at normal pressure ...................................................... [1] (1)
(ii) the
body temperature of a healthy person .................................................... [1] (1)
(iii) the
melting point of iron ................................................... [1] (1)
(iv) normal
room temperature .................................................. [1] (1)
(v) the
melting point of pure ice .................................................... [1] (1)
(b) State two ways in which a clinical
thermometer differs from a laboratory thermometer.
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
(c) What are the two most common liquids used in a
laboratory thermometer?
(2)
................................................................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................................................ [2]
TOTAL / 9
Low
Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET
20
Complete the following sentences.
______________________ currents form when liquids are heated.
The hot liquid
_____________ and the cold liquid ________________.
Energy travels
through space by ______________, which can be reflected by _________________.
Shiny surfaces are
_______________ and dull black ones are _________________.
The unit of energy
is the _______________.
Energy travels
through the bottom of a saucepan by _________________.
Metals are good
_______________ whereas plastics are good ______________. (11)
TOTAL / 11

![]()

![]()


![]()