| Questions | Answers | ||
|
1.
F |
What
do we call it when sounds bounce back from hard surfaces? |
|
echoes |
|
2.
F/H |
what
is refraction? |
|
When
rays of light change direction when they cross the boundary between one
transparent substance and another |
|
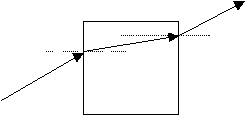
3.
F/H |
Draw
a diagram to show what happens to rays of light when they cross the
boundary between air and glass |
air glass |
|
|
4.
F/H |
Sounds
can also be refracted - true or false? |
|
TRUE |
|
5.
F/H |
How
do we measure the amplitude of a wave? |
|
the
maximum disturbance caused by a wave |
|
6.
F/H |
what
do we call the distance between a particular point on a wave and the
same point on the next? |
|
wavelength |
|
7.
F/H |
what
is frequency? |
|
number
of waves each second produced by a source |
|
8.
F/H |
Waves
transfer energy from a source to other places with matter being
transferred - true or false? |
|
false
- no matter is transferred |
|
9.
F/H |
what
causes a change in the direction of water waves when they cross the
boundary between two different substances? |
|
a
change in speed |
|
10.
F/H |
When
a ray of light travels from glass, 'Perspex' or water into air, all of
the wave is refracted - true or false? |
|
false
- some is reflected |
|
11.
F/H |
If
the angle between the ray and a normal is greater than a certain angle
(called the critical angle), all of the light is refracted inside the
glass, 'Perspex' or water. This is called total internal reflection -
true or false? |
|
false
- it's REFLECTED inside the glass |
|
12.
F/H |
what
is an optical fibre? |
|
all
the light may stay inside the fibre until it emerges from the other end
- light travels down optical fibres by repeated total internal
reflection. |
|
13.
F/H |
describe
a use for total internal reflection |
|
fibre
optic communications, medical exploration - needs a description |
|
14.
H |
are
sound waves longitudinal or transverse? |
|
longitudinal |
|
15.
H |
describe
the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves |
|
transverse:
wave motion is at right angles to the movement of the wave particles -
longitudinal: wave motion is along the same line as the motion of the
wave particles |
|
16.
H |
light
waves can travel throught a vacuum - true or false? |
|
TRUE |
|
17.
H |
light
waves are longitudinal - true or false? |
|
false
- transverse |
|
18.
H |
wave
speed is related to frequency and wavelength by an equation - what is
it? |
|
wave
speed = frequency x wavelength |
|
19.
H |
what
is diffraction? |
|
When
a wave moves through a gap, or
past an obstacle, it
spreads out from the edges |
|
20.
H |
can
electromagnetic waves and sound waves be diffracted? |
|
yes
- both of them - which is good eveidence that they travel as waves |
|
21.
H |
give
an example of the diffraction of sound: |
|
sounds
can sometimes be heard in the shadow of buildings; radio signals can
sometimes be received in the shadow of hills |
|
22.
H |
The
extent of this diffraction depends upon the wavelength of the waves -
true or false? |
|
TRUE |